Knowing how your computer works is very useful. It helps you use it better every day. Modern tech needs both physical parts and software to work well together.
This knowledge is great for fixing problems or upgrading your computer. It helps you understand how each part works together. This makes it easier to make smart choices about your computer.
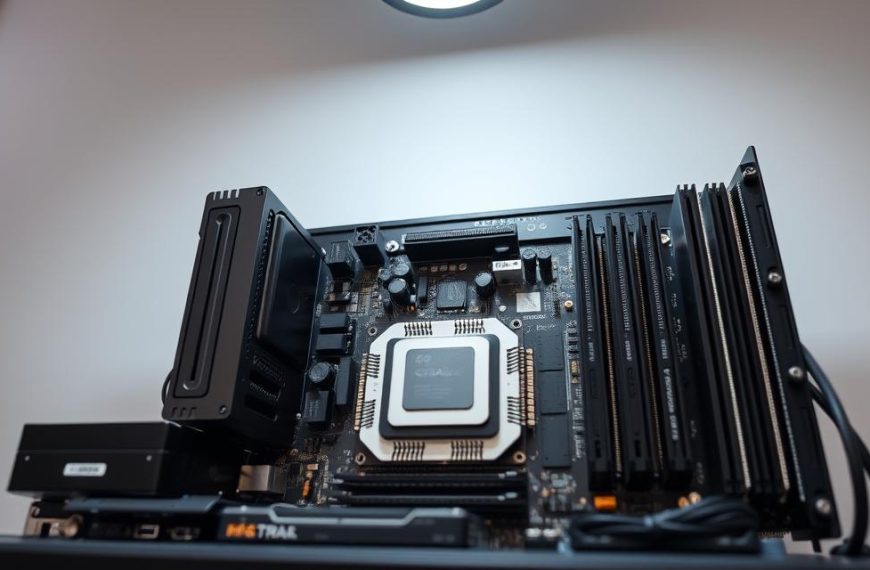
The key hardware parts are the motherboard, CPU, memory, storage, and power supply. Each one is important for the computer to work right.
We will look at these parts more closely in the next sections. We’ll see how they work together to give you computing power.
An Overview of Computer Systems
Computer systems are the heart of our digital world. They run complex algorithms and process information with ease. Their design ensures they work well in many different tasks.
Every computer has both internal and external computer hardware parts. The inside includes the motherboard, CPU, storage, and memory. These parts are the base for software to work on.
Hardware and software work together to make systems function. Hardware is the physical part, and software gives it instructions. This team effort lets computers do simple and complex tasks.
“The architecture of computer systems reflects an elegant balance between physical components and logical organisation, creating platforms capable of remarkable computational feats.”
Each part of the hardware has its own job in the system. Their quality affects how well the system works over time. Problems often come from parts not fitting together or getting old, showing why choosing good computer hardware is key.
| Component Type | Primary Function | Performance Impact | Common Variants |
|---|---|---|---|
| Processing Units | Execute instructions | Calculation speed | Single-core, Multi-core |
| Memory Modules | Temporary data storage | Multitasking capability | DRAM, SRAM |
| Storage Devices | Long-term data retention | Access speed | HDD, SSD |
| Connectivity Hardware | Component communication | Data transfer rates | PCIe, SATA |
Today’s systems share a common design, despite their differences. This makes them work well together, no matter who made them. The basic ideas are the same, from home computers to big business systems.
Knowing how systems are built helps us see how each part helps the whole. The next parts will look at these components more closely, showing what they do and how they work.
What Are the Five Main Components of a Computer System?
Every computer system has five key parts that work together. These are the motherboard, central processing unit, random access memory, storage devices, and power supply unit. They are the core of how computers work.
The motherboard is like the brain, linking everything together. It has paths for communication and holds important connectors. Without it, other parts can’t talk to each other.
Central processing units are the system’s brain. They carry out instructions and handle data from different programs. How fast the CPU is affects how well the system works.
Random access memory is for storing data temporarily. It’s lost when the power goes off. How much RAM you have impacts how many things you can do at once.

Storage devices keep data safe forever. Hard drives and solid-state drives hold the operating system, apps, and files. They keep your data safe even when the computer is off.
Power supply units turn electricity from the wall into the right kind for the computer. They make sure all parts get the power they need. A good PSU keeps the system running smoothly and prevents damage.
| Component | Primary Function | Performance Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Motherboard | Component interconnection | Determines upgrade options |
| CPU | Data processing | Affects calculation speed |
| RAM | Temporary data storage | Influences multitasking ability |
| Storage | Permanent data retention | Affects loading times |
| PSU | Power distribution | Ensures system stability |
These five parts make up a complete computer system. Each one is important for processing, storing, and managing digital info. Working together, they help computers do lots of things well.
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
The Central Processing Unit is the brain of any computer. It makes sure everything runs smoothly. It turns user commands into actions, essential for simple and complex tasks.
Definition and Primary Function
The CPU is like the computer’s brain. It follows a detailed process to execute commands. It does arithmetic and logical operations, driving all software.
It handles simple tasks like addition and complex tasks like graphics. The CPU’s speed affects how fast your system works.
Operation and Performance Metrics
CPU performance is measured in gigahertz (GHz). A higher GHz means faster processing. But, other factors also play a role.
Modern CPUs have multiple cores for better multitasking. This makes them more efficient at handling tasks at the same time.
Key performance indicators include:
- Clock speed (measured in GHz)
- Core count (dual-core, quad-core, etc.)
- Cache memory size
- Thermal design power (TDP)
Overclocking can boost CPU performance. But, it can also lead to overheating and damage.
Common CPU Types and Examples
The processor market is dominated by two main players. They offer different architectures and performance levels. Both cater to various needs and budgets.
Intel Core Series
Intel’s Core series processors are reliable and perform well across different tasks. The i7-12850HX is a top mobile processor. It has a hybrid architecture for better performance and efficiency.
This architecture helps manage power while keeping processing strong. Intel processors are great for single-threaded tasks and gaming.
AMD Ryzen Series
AMD’s Ryzen processors are known for their competitive prices and strong multi-core performance. They offer high core counts at various prices. This makes them popular among content creators and those who multitask a lot.
Ryzen processors are strong in multi-threaded tasks and energy efficiency. They support advanced technologies like simultaneous multithreading for better parallel processing.
Intel and AMD keep improving with each new generation. They push processor capabilities while keeping compatibility with existing systems.
Random Access Memory (RAM)
The CPU is like the brain of your computer. RAM is like its workspace, holding data for active programmes. It’s key to how well your system works.
Understanding RAM and Its Purpose
RAM is your computer’s short-term memory. It stores data for programmes to access quickly. Unlike hard drives, RAM loses all data when you turn off your computer. This makes it very fast for reading and writing.
The main purpose of RAM is to give the CPU quick access to data. When you open a programme, it loads into RAM, not from your hard drive. This makes your computer much faster.
Impact on System Performance
RAM affects how fast your computer responds and how well it can multitask. More RAM means you can run more programmes at once without slowing down. Not enough RAM makes your computer slow down, as it uses slower storage instead.
Today’s programmes and operating systems need a lot of memory. Web browsers, photo editing, and games all benefit from lots of RAM. Upgrading your RAM is often the best way to improve older systems’ performance.
Types of RAM Modules
RAM technology has changed a lot, with DDR4 and DDR5 being the latest. Each new generation is faster, uses less power, and holds more data than the last.
DDR4 Technology
DDR4 became popular around 2014 and is widely used today. It’s faster and uses less power than older RAM. You can find DDR4 modules from 4GB to 16GB, with speeds from 2133MHz to 3200MHz.
DDR4 supports bigger memory chips, making it possible for larger modules. Most motherboards today support DDR4, making it a good choice for many.
DDR5 Technology
DDR5 is the newest memory technology. It’s faster, uses less power, and holds more data than DDR4. DDR5 starts at 4800MHz and can go up to 6400MHz or more.
DDR5 has on-die error correction and dual 32-bit channels for better efficiency. It’s pricier than DDR4 but is better for high-end systems and gaming.
When picking between DDR4 and DDR5, think about your motherboard, needs, and budget. DDR5 is better for demanding tasks, but DDR4 is more affordable and reliable.
Storage Devices
Storage devices are like the long-term memory of your computer. They keep your data safe even when the power is off. Unlike RAM, which holds information temporarily, these devices store your operating system, apps, and files forever.
Today’s computers use two main types of storage devices: hard disk drives and solid state drives. Each has its own benefits for different needs.
Hard Disk Drives (HDDs)
Hard disk drives have been around for decades. They store data on magnetic platters that spin fast. Read/write heads skim the surface to access information.
HDDs are great value for money. They cost less per gigabyte than SSDs. You can get huge storage, like 1TB or 2TB, without spending a lot.
But, HDDs have downsides. They’re more prone to damage from shocks or drops. They also read files slower than SSDs.
Solid State Drives (SSDs)
Solid state drives are the newer, faster option. They use flash memory chips, not moving parts. This makes them faster and more durable.
SSDs are super fast. They make computers boot up and load apps quickly. They’re also tough and can handle bumps better.
But, SSDs are pricier per gigabyte. They also have smaller max capacities than top HDDs.
Choosing Between HDD and SSD
Choosing the right storage depends on your needs and budget. Most computers use both HDD and SSD for the best performance.
For those on a budget or needing lots of storage, HDDs are a good pick. They’re perfect for big media collections and archives.
SSDs are better for fast, frequent use. They make computers feel quicker and more efficient.
Many people choose a mix: a small SSD for the OS and apps, and a big HDD for storage. This combo offers speed and space at a good price.
| Feature | Hard Disk Drives (HDD) | Solid State Drives (SSD) |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | Magnetic spinning platters | Flash memory chips |
| Speed Performance | Slower (typically 100-150 MB/s) | Faster (500-3500 MB/s) |
| Durability | More vulnerable to physical shock | More resistant to physical damage |
| Cost per GB | Lower (£0.02-£0.03/GB) | Higher (£0.08-£0.15/GB) |
| Power Consumption | Higher (6-7 watts) | Lower (2-3 watts) |
| Noise Level | Audible spinning and seeking | Silent operation |
The world of storage is always changing. New tech promises even better performance and reliability. Knowing about HDDs and SSDs helps you make smart choices for your computer.
Motherboard
The motherboard is key in making all parts of a computer work together. It acts as a central hub, connecting everything. It has spots for components and paths for data to flow.
Role of the Motherboard
The motherboard’s main job is to manage data between all parts of the system. It gets power from the PSU and helps different parts talk to each other.
Imagine it like a city’s roads. Data buses are the highways, and the chipset is the traffic light. This keeps everything running smoothly in your computer.
Key Motherboard Components
Modern motherboards have special areas that affect how well they work. Knowing about these is important when choosing or upgrading your system.
CPU Socket and Chipset
The CPU socket connects your processor physically and electrically. It’s specific to certain CPU types from Intel or AMD. The chipset controls data flow between parts, like a brain.
Expansion Slots and Connectors
Expansion slots let you add new features with cards like GPUs. PCIe slots are the latest, with different speeds. SATA ports connect storage drives, and front-panel headers control case features.
Motherboard Form Factors
Form factors set the size and mounting points of motherboards. Common sizes for desktops are:
- ATX: Full-size boards with lots of slots
- MicroATX: Smaller version with fewer slots
- Mini-ITX: Very small for tiny builds
Laptop motherboards have their own sizes, matching the laptop’s design. Make sure the size fits your case before buying.
Power Supply Unit (PSU)
The Power Supply Unit is the heart of your computer’s electrical system. It changes alternating current from your wall outlet into direct current for your components. Without a reliable PSU, even the most powerful components can’t work right.

Function of the PSU
A PSU’s main job is to convert and distribute power. It changes the 110-120V AC power from your mains into lower voltage DC power that computer parts need.
The unit has multiple voltage rails: +3.3V, +5V, and +12V for different parts. Modern PSUs also have protection features like over-voltage, under-voltage, and short-circuit protection to keep your hardware safe.
Types of Power Supplies
There are two main types of PSUs that affect cable management and system building. The choice between them greatly impacts your computer’s internal organisation and airflow.
Modular PSUs
Modular power supplies offer great flexibility by letting users connect only the cables they need. This design reduces clutter and improves airflow in your computer case.
These units cost more but offer cleaner installations. They’re best for custom builds where looks and airflow are important.
Non-Modular PSUs
Non-modular PSUs have all cables permanently attached to the unit. While they might make cable management harder, they’re often more affordable.
These power supplies are fine for standard builds where looks aren’t as important. The fixed cable design also means you won’t lose any cables.
Selecting the Right PSU
Choosing the right Power Supply Unit involves several key factors. Your choice should match your system’s needs and allow for future upgrades.
Wattage calculation is key – estimate your components’ total power use and add 20-30% extra. Online PSU calculators can help figure out what you need.
Efficiency ratings are important for performance and saving on electricity. Look for units with 80 Plus certification (Bronze, Silver, Gold, Platinum, or Titanium). Higher ratings mean better energy conversion and less heat.
Consider these extra factors when picking your PSU:
- Connector types and quantities for your specific components
- Warranty length and manufacturer reputation
- Noise levels from the cooling fan
- Physical dimensions to ensure case compatibility
Investing in a quality Power Supply Unit protects your entire system and ensures stable operation under all conditions. Never compromise on this critical component.
Interaction of Components in a Computer System
Learning how computer parts work together shows the magic of computing. Each part joins to form a system through smart communication and data flow. This teamwork turns separate parts into a strong computing machine.
Data Flow and Communication
The motherboard is like the brain of the computer. It has paths and rules for data sharing. Components use special buses and interfaces to send and receive information.
Key communication channels include:
- Front-side bus connecting CPU to RAM
- SATA interfaces for storage devices
- PCI Express slots for expansion cards
- Power connectors distributing electricity
This network lets each part get what it needs. The smooth data flow boosts system performance. Today’s computers use advanced protocols to avoid slowdowns.
Practical Example: Running an Application
Starting a programme like a web browser is a complex process. It involves many component interactions in your system.
It starts when you click the icon. Your storage device sends the programme files to RAM. The CPU then runs these instructions, working with other parts.
During programme execution:
- PSU provides stable power to all active components
- Motherboard facilitates communication between parts
- RAM stores temporary data for quick access
- CPU processes instructions and manages operations
This teamwork shows how parts rely on each other. The system’s success depends on good data flow and resource use. Knowing about computer basics helps us see their connection.
Even simple tasks need great teamwork from hardware. This teamwork makes modern computing work, even though it’s complex.
Conclusion
Learning about the five key parts of a computer is vital. The CPU, RAM, storage, motherboard, and PSU all work together. They make sure your computer runs smoothly.
Knowing how these parts work is key when you face problems or want to upgrade. It helps you find and fix issues quickly. It also helps you choose the right upgrades for your needs.
Looking after your computer’s parts can make it last longer. Keeping them clean and checking their temperature helps avoid damage. Choosing top brands like Intel, AMD, Samsung, and Corsair can also improve your computer’s performance.
When you think about upgrading, think about what will help you the most. For gamers, getting a better GPU and CPU is important. For those who work a lot, more RAM and faster storage can make a big difference.
Spending time to learn about computer parts can really pay off. It helps your computer run better and last longer. This knowledge lets you upgrade wisely and keep your system in top shape.
FAQ
What are the five main components of a computer system?
The main parts are the motherboard, CPU, RAM, storage devices, and PSU. They work together to run programmes and process data well.
Why is it important to understand these computer components?
Knowing these parts helps with fixing problems, upgrading, and improving performance. It also helps when buying or maintaining a computer.
What is the difference between volatile and non-volatile memory?
Volatile memory, like RAM, loses data when power is off. Non-volatile memory, such as storage devices, keeps data even without power. This affects how data is stored and accessed.
How does the CPU contribute to a computer’s performance?
The CPU handles operations and instructions. Its speed and number of cores, like in Intel Core i7-12850HX or AMD Ryzen series, affect performance.
What role does RAM play in system performance?
RAM gives quick access to data, improving performance. Not enough RAM can cause crashes or slowdowns. Upgrading to DDR4 or DDR5 can greatly improve efficiency.
Should I choose an HDD or an SSD for storage?
HDDs are cheaper but slower. SSDs are faster and better for tasks like gaming. Choose based on budget, speed needs, and use, like a 1TB HDD for storage or an SSD for quick access.
What is the function of the motherboard in a computer system?
The motherboard connects components like the CPU, RAM, and storage. It has key parts like the CPU socket, chipset, and expansion slots for add-ons.
How do I select the right power supply unit (PSU)?
Pick a PSU based on your system’s wattage, efficiency, and whether you prefer modular or non-modular. A good PSU ensures stable operation and protects components.
How do the components interact when running an application?
When running an app, the CPU processes instructions, RAM stores data, storage devices retrieve files, and the PSU powers components. The motherboard coordinates this for smooth operation.
What are common motherboard form factors, and how do they affect compatibility?
Form factors like ATX and microATX differ in size and features. Larger ones offer more slots, while smaller ones fit compact cases. Choose based on your case and components.
What risks are associated with overclocking a CPU?
Overclocking can boost performance but may cause overheating and damage. It needs good cooling and careful settings to avoid harm.
Can upgrading RAM improve an older computer’s performance?
Yes, upgrading RAM can make an older system run better. It allows more programmes to run at once and reduces lag. It’s a cost-effective way to keep an older system running.